Create a signed check request
This topic illustrates how to create a signed check request to an integration.
For details on how you can validate these requests, see Validate check requests from Maxsight.
To create a signed check request:
If applicable, create the payload
digest.This is done using a Base64 encoded, SHA-256 hash digest signature of the payload. The created digest then has
SHA-256=appended to it to create the fulldigestheader value. Thisdigestallows us to check the data hasn't been changed since the original request.For example, a payload digest might be:
SHA-256=60qYX1UaBLyxC+NNCD5+FDbNGi/eSEdms395N3KmJ2M=Create a bytes string using the check request signature headers.
The format used should be
header: valuewith each header/value pair joined by a new line character.For example, if we had a check request with the following details:
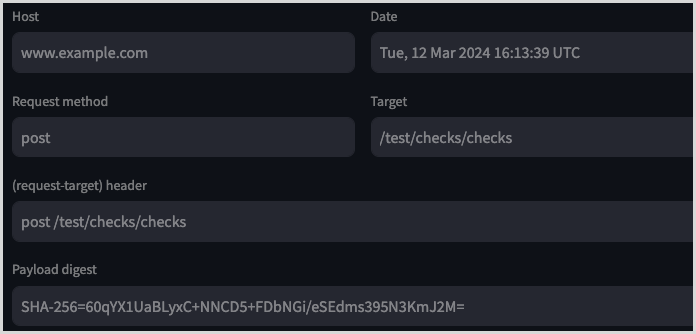
Our bytes string would look like the following. Note the /n characters indicating a new line):
b'(request-target): post /test/checks/checks\nhost: http://www.example.com \ndate: Tue, 12 Mar 2024 16:13:39 UTC\ndigest: SHA-256=60qYX1UaBLyxC+NNCD5+FDbNGi/eSEdms395N3KmJ2M='Create the
Authorizationheader value using the bytes string created in step two.Create a
signatureby creating a HMAC from the bytes string in step two. The new HMAC key should be the Base64 decodedSECRET_KEYshared between Maxsight and the integration.Once the
signatureis created, it should be placed in theAuthorizationheader along with theKeyId,algorithm, and theheadersused to create the headers bytes string. TheAuthorizationheader should start with the valueSignatureand then include theKeyId,algorithm,signature, andheadersin that order, all prefixed with an = symbol and wrapped in double quotes.The output could look like the following:
Signature keyId="P1WXsqXZ",algorithm="hs2019",signature="EKtr9aSxFsQAe7ABytKrRYhrE/aTMIDdc2WpAy4gcCI=",headers="(request-target) host date digest"
Example
Using the previous procedure, here is an example output of a signed check request, showing the request headers and payload.
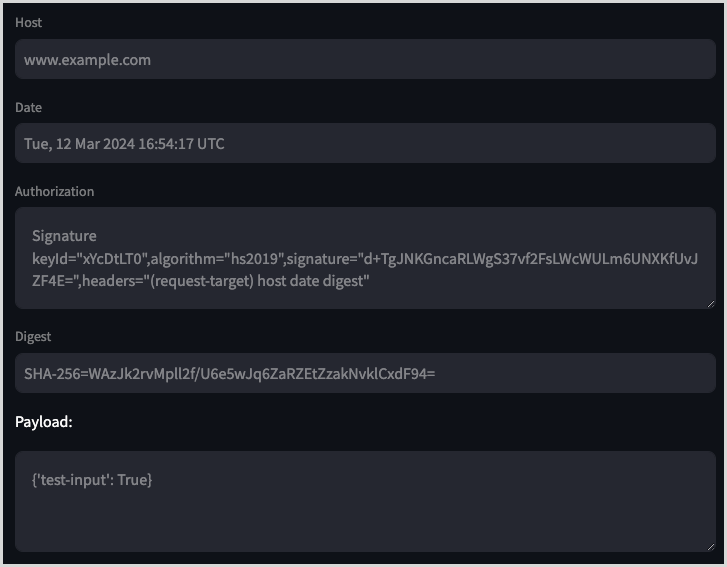
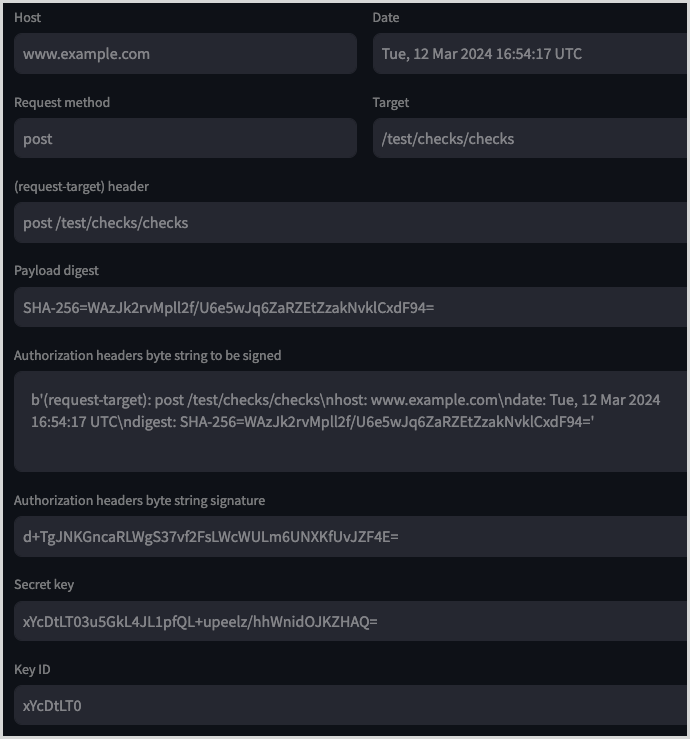
The following image shows a breakdown of how these values were created:
Code example
The following example shows how a check request could be signed using Python:
from datetime import datetime, timezone
import hmac
import hashlib
import base64
# set the secret key
SECRET_KEY = 'your-base64-encoded-secret-key-here'
# decode the secret key
decoded_secret_key = base64.b64decode(SECRET_KEY)
# the host will be as per specified in request header
HOST = 'your-integration-host.com'
# the target will be as per specified in request header
TARGET = '/your-endpoint-target/checks'
# the date will be set using UTC and the format below
# as an example this presents as: 'Fri, 06 Oct 2023 12:27:32 UTC'
DATE = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S %Z').strip()
# generate the digest from the request payload
request_payload = <the data you want to send in your request payload>
DIGEST = base64.b64encode(hashlib.sha256(request_payload).digest()).decode()
# the headers should be all headers to be signed, NOTE THE NEW LINE CHARACTERS AND SPACES,
# ensure the method is included before the target: e.g 'get /your/endpoint/target'
headers_str = f'(request-target): post {TARGET}\nhost: {HOST}\ndate: {DATE}\ndigest: SHA-256={DIGEST}'
# encode the string into bytes
headers_str_as_bytes = headers_str.encode()
# this will be how the signature in the Authorization header will be generated
# create the hmac, note, use the decoded secret key, and a supported sha256 digest
new_hmac = hmac.new(key=decoded_secret_key,
msg=headers_str_as_bytes,
digestmod=hashlib.sha256).digest()
# encode the hmac, note for usual requests to your integration,
# url_safe is NOT used for standard requests
signature = base64.b64encode(new_hmac).decode("utf-8")
# create the authorization header value
authorization = f'Signature KeyId="{SECRET_KEY[:8]}",algorithm="hs2019",signature="{signature}",headers="(request-target) {headers_string}"'
# set the request headers
headers = {"Date": DATE,
"Authorization": authorization,
"Digest": f"SHA-256={DIGEST}"}
# create prepared request
output = requests.Request(method="post", url=url, headers=headers, json=payload)
prepared_request = output.prepare()
# send the prepared request
with requests.Session() as session:
response = session.send(prepared_request)